CURRENT ISSUE
November, 2025
No. 110 (11)
2024 Impact Factor: 7.9
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
EDITOR'S PICKS
Review Series on Histiocyte Society
Introduction to the Review Series. Looking back and to the future: the Histiocyte Society blueprint for research in histiocytic disorders
Histiocyte Society blueprint for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis research: deciphering underlying disease mechanisms to optimize diagnosis and therapy
Histiocyte Society blueprint for Langerhans cell histiocytosis research: from cell-of-origin to a more comprehensive cure
Histiocyte Society blueprint for non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis research: unraveling complex diseases through collaboration
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
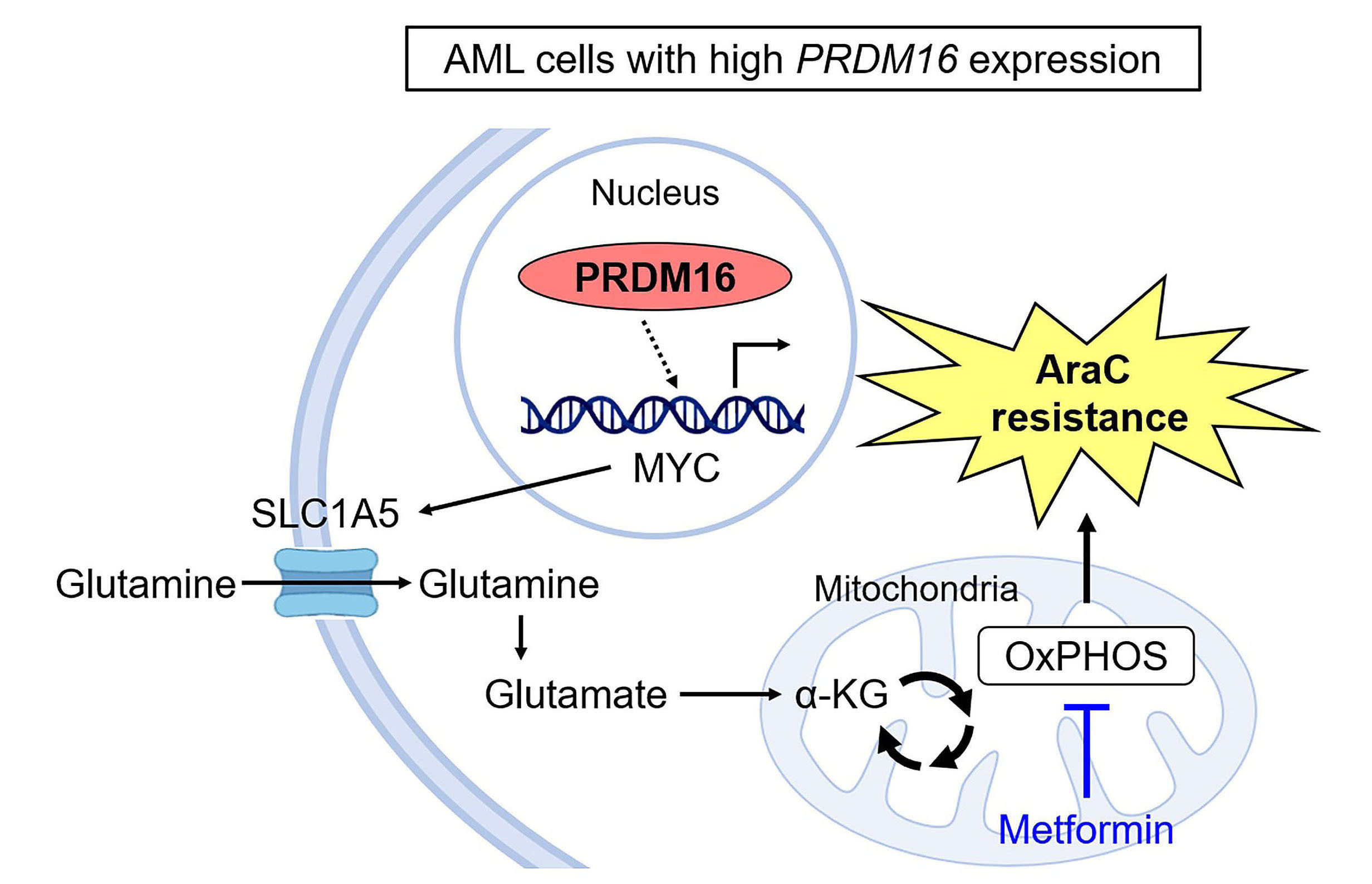
Metabolic reprogramming by PRDM16 drives cytarabine resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
A high PRDM16 expression is predictive of induction failure in both pediatric and adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Ikeda and colleagues performed cell viability, transcriptome, metabolome and in vivo analyses using both murine leukemic cells and patients’ samples and explored response to chemotherapy in leukemic cells with high expression of the short isoform of PRDM16 (sPRDM16). Their study uncovered unique sPRDM16-driven metabolic reprogramming, leading to chemoresistance of AML cells with high sPRDM16 expression.
Article
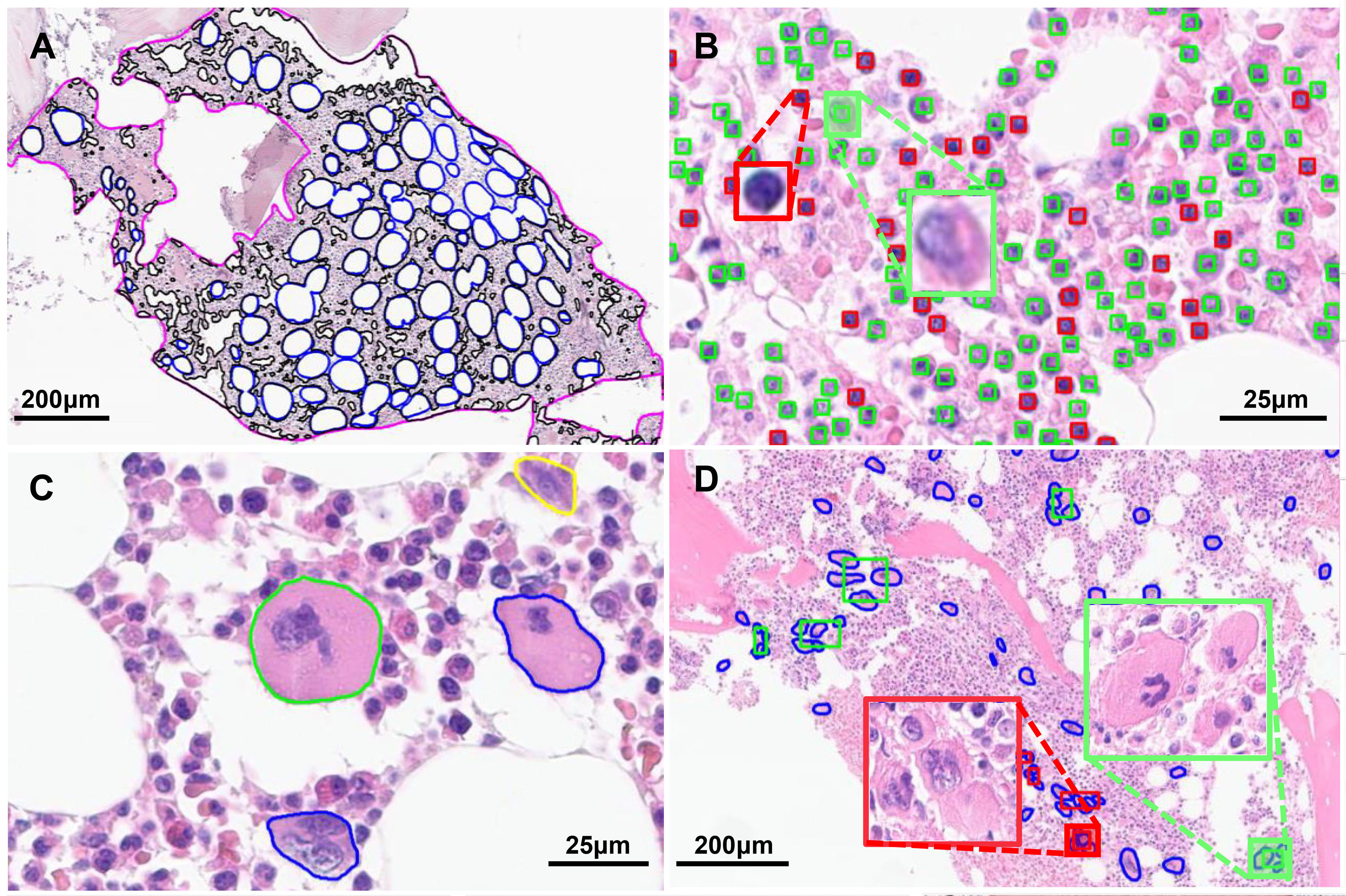
Artificial intelligence-based quantitative bone marrow pathology analysis for myeloproliferative neoplasms
The integration of clinical, laboratory, and histopathological characteristics is required for accurate diagnosis and categorization of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). Yu and colleagues developed advanced algorithms with the aim of assisting hematopathologists in the detailed quantitative analysis of bone marrow trephine samples for classifying MPN. Artificial intelligence was used to create an auxiliary diagnostic platform highly accurate for quantitatively analyzing bone marrow pathology and classifying MPN subtypes and non-neoplastic cases.
Article
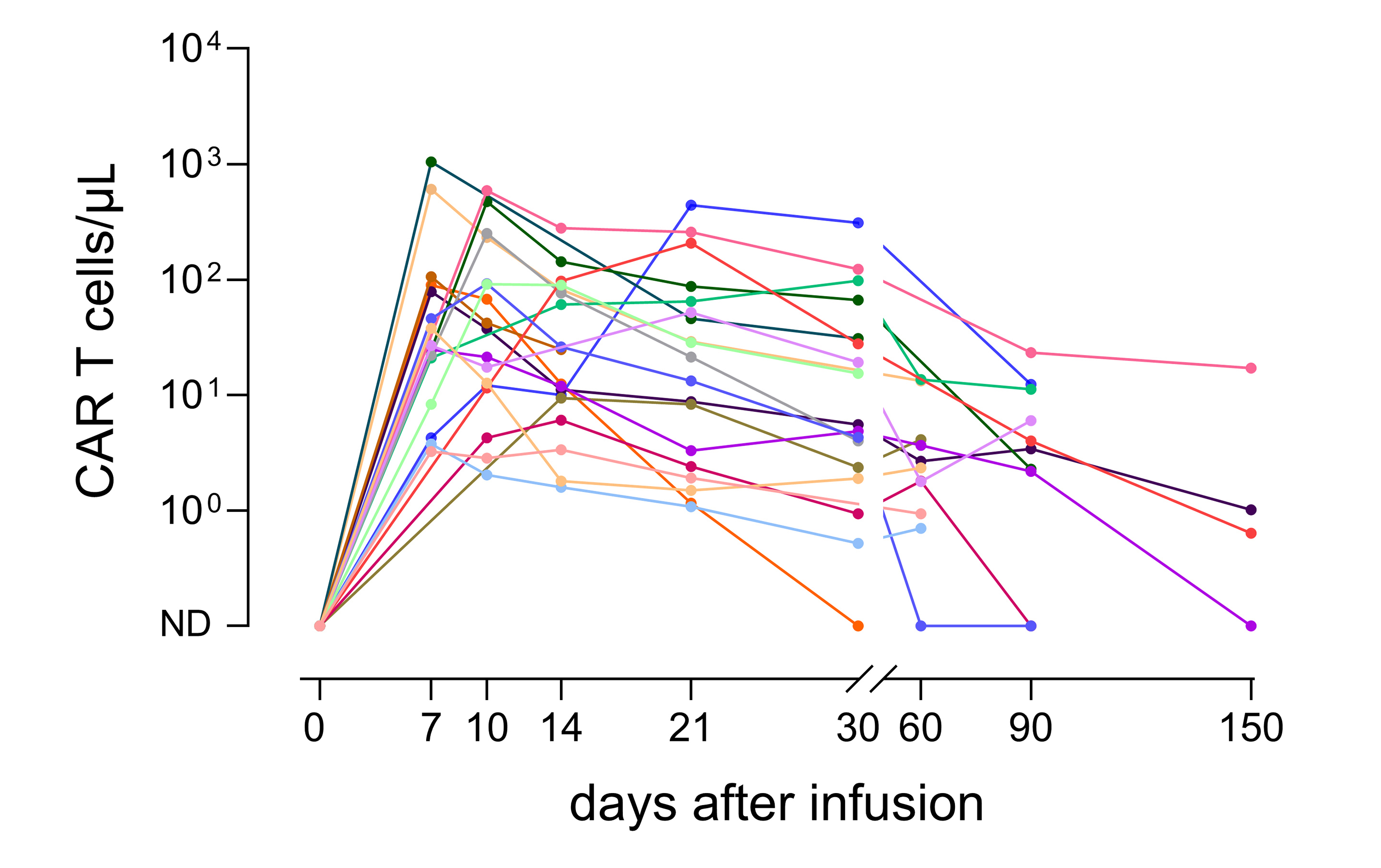
CAR T expansion and systemic inflammation: diverging impacts on large B-cell lymphoma therapy in the multicenter CART SIE study
Clinical response to CD19-directed T-cell therapy is strongly linked to the T cells’ in vivo expansion and persistence, as demonstrated in clinical trials. Magni and colleagues conducted an analysis on CAR T expansion kinetics in a cohort of 262 patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma, and investigated the relevance of CAR T subpopulations in mediating the therapeutic efficacy. The results showed that CAR T-cell therapy efficacy depends not only on robust expansion but also on the phenotypic quality of CAR T cells and the systemic inflammatory state.
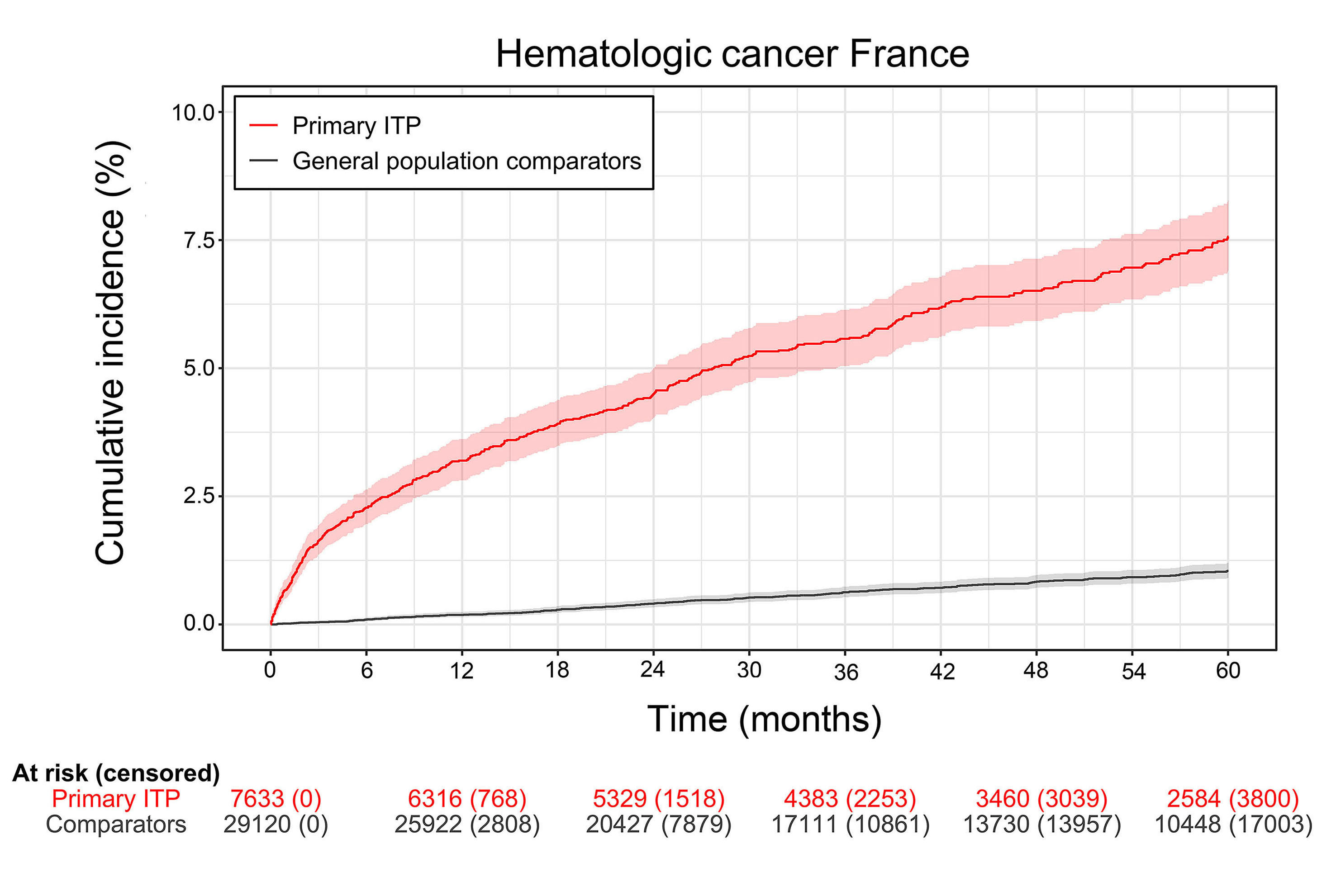
Article
Risk of cancer in adults with primary immune thrombocytopenia: a binational population-based realworld cohort study from Denmark and France
Do the immune dysregulation and immunosuppression related to the pathophysiology and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) increase the risk of cancer? Mannering and colleagues conducted a real-world study with a binational cohort to investigate the risk of solid and hematologic cancers in patients with ITP compared with the general population in Denmark and France. The results showed an increased risk of cancer following ITP compared to that in the general population, with the risk of hematologic cancer increased above all.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA